Top-10-Machine-Learning-Algorithms-Beginners-Should-Know-5
Bagging and Random Forests
Random Forest is one of the most popular and powerful machine learning algorithms. It is an integrated machine learning algorithm. It is called Bootstrap Aggregation or bagging.
Bootstrap is a powerful statistical method for estimating quantities from data samples.
In bagging, the same method is used, but for estimating the entire statistical model, most often a decision tree.
** Get multiple samples of the training data and then build a model for each data sample. When you need to make predictions for new data, each model makes predictions and averages the predictions to better estimate the true output values. **
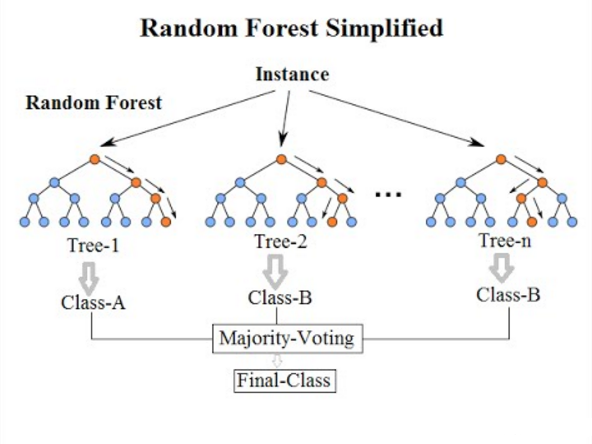
Random forests are an adaptation of this approach in which decision trees are created so that instead of selecting the optimal segmentation points, sub-optimal segmentation is performed by introducing randomness.
As a result, the model created for each data sample is more different compared to the others, but still accurate in its own unique and different way. Combining their predictions gives a better estimate of the true potential output values.
Boosting and AdaBoost
**Boosting is an integration technique that attempts to create a strong classifier from multiple weak classifiers. **
This is done by building a model from the training data and then creating a second model to try to correct the errors in the first model. Models are added until the training set is perfectly predicted or the maximum number of models are added.
AdaBoost was the first really successful boosting algorithm developed for binary classification. It is the best starting point for understanding boosting.
AdaBoost works with short decision trees.
After the first tree is created, the performance of the tree on each training instance is used to measure how much attention the next tree created should pay to each training instance. Training data that is difficult to predict is given a higher weight, while instances that are easy to predict are given less weight.
Models are created sequentially one after the other, and each model updates the weights on the training instances that affect the learning performed by the next tree in the sequence.
After all trees have been constructed, predictions are made on new data and the performance of each tree depends on how accurate it is on the training data.
Since the algorithm puts a lot of emphasis on correcting errors, it is important to have clean data and remove outliers.